Concerns and Complications of Measles and Mumps
March 1, 2023
Reprints
Related Articles
-
Is Artificial Intelligence Coming for Your Job?
-
Can Pulmonary Artery Pressure Help in the Decision to Operate in Chronic Aortic Regurgitation?
-
Combined TAVR and LAAO Studied in a Randomized Controlled Trial
-
Another Hemodynamic Variant of Aortic Stenosis
-
Clinical Features of Tachyarrhythmia-Induced Cardiomyopathy
AUTHOR
Trahern W. Jones, MD, Assistant Professor, Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases, University of Utah Health, Salt Lake City
PEER REVIEWER
Glen D. Solomon, MD, FACP, Professor and Chair, Department of Internal Medicine, Wright State University Boonshoft School of Medicine, Dayton, OH
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- Since early 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic has created major delays and disruptions in global childhood immunizations, adding to the risk of new outbreaks of diseases that previously had been well-controlled.
- Prior to measles vaccine, the United States recorded 3 million to 4 million cases of measles per year. Typical complications of disease included 48,000 hospitalizations, 1,000 cases of encephalitis, and 400-500 deaths per year.
- After the introduction of effective vaccines, measles incidence in the United States dropped by more than 99% to an all-time low of 37 cases between 2000 and 2007, with measles deaths essentially eliminated.
- Similarly, with mumps vaccination the United States experienced a 97% decrease in mumps cases, and by 2001-2003 the United States reported fewer than 300 cases each year.
- Measles is one of the most infectious agents known to medicine, with nearly 90% of unimmunized individuals expected to contract the disease after exposure to an active case.
- After immunization with two doses of measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, protection against acquiring and transmitting measles is 97% and long-lasting.
- However, protection against mumps peaks at 88% and declines during adolescence and young adulthood, creating the potential for outbreaks.
Since early 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic has led to major delays and disruptions in global childhood immunizations. Decreased vaccine coverage against diseases such as measles and mumps has led to new vulnerabilities in pediatric population health. Thus, the astute practitioner should be vigilant and ready to recognize and diagnose these infections at home and abroad.
Measles and mumps, while clinically dissimilar, share important characteristics that are valuable to discuss in tandem. Both are members of the virus family Paramyxovidiridae, both were historically common causes of morbidity and mortality in childhood, and both have been major targets of national and global vaccination campaigns. This review will seek to inform the practitioner about current outbreak concerns regarding measles and mumps, clinical manifestations and complications of each, diagnostic and treatment options, and, ultimately, prevention of further exposures.
Measles
Past/Global Epidemiology
Measles is one of the most infectious agents known to human medicine.1 When exposed to a patient with an active case of disease, nearly 90% of unimmunized individuals can be expected to contract the disease.2 From another epidemiologic perspective, the basic reproduction number (R0) is the number of unimmunized individuals in a given setting who may contract the disease when exposed to an active case.1 In different outbreaks, the R0 reported for Ebola virus in the 2014 West African epidemic was 1.5 to 2.5; for smallpox, the R0 has been reported as 5-7.1,3 The R0 of the ancestral strain of SARS-CoV-2 was calculated to be 2.8, and the Delta variant was approximately 5.4 In contrast, the R0 for measles often ranges from 12 to 17 and may even exceed 30, depending on the outbreak and the circumstances of exposures.5
Before the modern era of vaccines, measles was a common childhood ailment, with major outbreaks surging every two to five years.1,6 Nonimmune and nonexposed birth cohorts of children would accumulate and experience a rise in the rate of endemic transmission, with a subsequent fall in the number of susceptible individuals.1,6 Notably, isolated communities that were left sheltered from these epidemiologic surges would accumulate large populations of vulnerable adults and children, and when the measles virus reached these communities, substantial mortality rates would result. For example, past records indicate a mortality rate of 10% to 33% in the Hawaiian Islands from the outbreak of 1848, while outbreaks in the Faroe Islands in 1846 led to similarly high rates of deaths.7,8 Measles also is implicated alongside smallpox as one of the major illnesses that led to the depopulation of the New World following European contact.9
Prior to the development of the measles vaccine, the United States generally recorded 3 million to 4 million cases of measles per year.10 Typical complications related to the high incidence of disease included 48,000 hospitalizations, 1,000 cases of encephalitis, and 400-500 deaths per year. After the introduction of the first licensed measles vaccine in 1963, and particularly after schools began requiring proof of immunization in the 1980s and the two-dose schedule was implemented, measles incidence in the United States dropped by more than 99% to an all-time low of 37 cases between 2000 and 2007.11,12 Similarly, measles deaths were essentially eliminated. The United States was declared measles-free, in the sense that endemic transmission had been fully ended.
Present Outbreaks
Since 2010, numerous cases and outbreaks have taken root in the United States as the result of importations of the virus from abroad.13,14 Many of these cases occurred among children or adolescents with no history of measles immunization or an unknown history of immunization. Successive years saw subsequent rises in case rates in the United States and Canada. By 2011, U.S. cases had risen to 118, the highest since 1996.13 In 2013, 2014, and 2015, the United States saw several dozen outbreaks, including epidemics among the historically unvaccinated Amish community, as well as the notorious multistate outbreak linked to an exposure at Disneyland theme parks in California.15,16
Unfortunately, the COVID-19 pandemic has led to numerous disruptions in routine childhood immunizations both in the United States and abroad. As providers’ offices closed and public health resources were diverted to handle the pandemic, children were left unimmunized and vulnerable to new measles outbreaks. In June 2022, it is estimated that 41 different countries put off their routine measles immunization campaigns.17 Now that many regions have stopped pandemic-related restrictions on school attendance, public gatherings, and travel, the measles virus is spreading rapidly through unimmunized populations. Nigeria, India, Somalia, and Ethiopia have tallied tens of thousands of measles cases from November 2021 to April 2022, while cases are rising in many other regions in Africa and Asia.17 These outbreaks soon may gain footholds in unvaccinated U.S. communities.
Acquisition and Incubation Period
Measles virus is transmitted through the production of aerosolized droplets from respiratory tract secretions.1,18,19 This occurs primarily through coughing and sneezing among infected, symptomatic individuals. Patients generally are contagious from four days prior to through four days after the onset of rash.19 With coughing and sneezing, larger droplets may land on potential new hosts within a short range, or smaller droplets may remain suspended in air, where they are inhaled into new hosts’ respiratory tract epithelia.18,20 These transmission pathways imply that both standard and airborne precautions are essential when dealing with potential measles cases.20
Measles virus appears to initially infect the respiratory tract epithelia of susceptible hosts.18 Once the virus is acquired, it quickly moves past the epithelium to local lymphoid cells and thereafter to the lymphatics serving the respiratory tract, and viremia ensues.21 This sequence of events occurs during the first three days of the incubation period. The virus then begins to multiply within respiratory tract epithelia and the reticuloendothelial system. From here, a secondary viremia may be generated, and clinically apparent infection ensues. In total, the typical incubation period lasts about eight to 12 days from the acquisition of the virus to the first presentation of clinical symptoms.19
Prodrome: Days 1-3 of Clinical Symptoms
The initial symptoms of clinical measles include early fever, malaise, cough, coryza (inflammation and congestion of the upper respiratory tract, often with rhinorrhea), and conjunctivitis. The classic enanthem of measles, Koplik spots, also may arise in the prodromal period. Although many of these symptoms may be explicable by other, more common and less consequential childhood respiratory viruses, the astute clinician should take a guarded approach in dealing with unvaccinated children, or when working in areas with active outbreaks or endemic infection. Therefore, the more nuanced characteristics of these symptoms should be explored in detail.
Fever in the prodromal period of measles begins early and increases steadily over the course of three to four days to an average high of 39.5°C.22,23 While the nasal symptoms of congestion and rhinorrhea are essentially indistinguishable from any other respiratory tract viral infection, the cough is especially irritating, worsening throughout the prodrome, and may have a brassy character. The conjunctivitis is especially intense; photophobia may be associated, along with copious lacrimation. Under slit-lamp examination, conjunctival and corneal lesions may be evinced, thus demonstrating the somewhat reliable presence of viral keratoconjunctivitis as a sign of measles infection.24
Practitioners should be attentive to the oral cavity of any child with symptoms suggestive of the prodrome of measles. Koplik spots are present in more than 70% of patients with measles.25 Most often, these are described as blue-white specks, 1 mm in diameter at the greatest, superimposed on bright red oral mucosa.26 The blue component often is not perceived, and most practitioners endorse that these spots are simply whitish in color, and in appearance may seem little more than flecks of sand.22,23 Koplik spots initially arise on the buccal mucosa opposite the mandibular molars, an area that is easily overlooked during the oral examination in most emergency room settings. Therefore, careful inspection with the aid of a gloved finger or tongue depressor is essential to visualize this sentinel region of mucosa for the presence of Koplik spots. From this somewhat small area of buccal mucosa, some individuals may experience the multiplication, coalescence, and spread of Koplik spots over the rest of the buccal and labial mucosa during the next 12 hours, but this may be missed by both parents and practitioners.22
Exanthem Period: Days 3-5 of Clinical Symptoms
The Koplik spots quickly fade by the time the classic measles exanthem begins on days 3 through 4. The rash appears initially behind the ears and at the hairline of the forehead, spreading cephalocaudally until by day 5, the face, neck, trunk, and extremities are covered.22,23 The rash is initially erythematous, morbilliform, and maculopapular in appearance, but during its spread begins to coalesce, particularly over the face and trunk. (See Figure 1.) The color gradually turns from a bright erythematous appearance on the first day, until day 5, when it takes on a more brownish, coppery, or dusky hue.22
Figure 1. Coalescent Measles Rash |
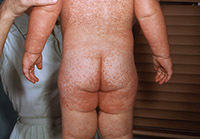 |
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Public Health Image Library |
This also is the period when the fever of measles peaks and eventually breaks, with temperatures falling off after the fourth day. Likewise, nasal and upper respiratory symptoms will diminish as well, save for a possible lingering cough. The conjunctivitis typically will resolve by the fifth day. There may be some ongoing pharyngitis and diffuse lymphadenopathy as well. Ongoing fevers or worsening cough should suggest the patient is experiencing a complication of measles, such as pneumonia, and management should be tailored accordingly.
Clearance: Days 5-7
After the rash coalesces and turns dull in color, it will begin to clear in a similar pattern to its appearance. Notably, the rash typically only coalesces across the central regions of the body, but spots remain discrete in peripheral locations. As the rash clears cephalocaudally, some individuals may experience desquamation in the most severely affected regions, although this is not a common pattern.22
By day 7, the rash is expected to be almost fully cleared, and many of the most bothersome symptoms of the prodrome, such as fever, rhinorrhea, and conjunctivitis, are expected to fade. As mentioned before, ongoing fevers after days 4 and 5 should alert the practitioner to possible complications. Parents should expect the child to have a lingering cough for the following one to two weeks, as with any viral respiratory illness.
Modified and Atypical Measles
Individuals with partial immunity can develop modified measles, a clinical illness with an altered presentation. The course is significantly milder but still follows the general pattern of classic disease. Patients may experience a much shorter prodrome, and typical symptoms of cough, fever, conjunctivitis, and congestion may be much less apparent.22,23 Koplik spots may be reduced or absent, and the rash, while possibly still present, may not achieve coalescence. Modified measles is rare. However, it may be observed in infants with the clinical disease but with lingering transplacental maternal immunity, or it may occur because of secondary vaccine failure.
Atypical measles largely is a historical curiosity, the product of prior immunization campaigns and modified immunological activity with inactivated or “killed” measles vaccine (KMV).27 Only 600,000 to 900,000 people received KMV between 1963 and 1968, and there have been few, if any, cases of atypical measles since the 1980s.28 The syndrome was characterized by a number of unique manifestations, most prominently a “reverse” rash that progressed from the extremities cephalad rather than cephalocaudally, as seen in classic measles.22,27 KMV was taken off the market after 1967, and the current measles vaccine is a live, attenuated vaccine.
Complications
Complications from natural measles infection are a frequent occurrence. Some of the most common complications are relegated to the respiratory tract, and many children will experience secondary otitis media, as well as laryngitis and laryngotracheobronchitis during or after the resolution of the main viral illness.22 Half of all children with measles virus infection may develop radiographic evidence of viral pneumonia, even if their disease is relatively mild.29
Most worrisome, however, is the development of a secondary bacterial pneumonia, which is by far the leading cause of mortality in all measles cases around the world.22,30 Potentially one in 20 children with measles virus infection may develop clinical pneumonia.31 Practitioners should be alert to the continuation of fever beyond day 4, or potentially the development of a “biphasic” illness, in which the child experiences new fevers five to 10 days after the initial symptoms of measles.
The gastrointestinal tract also is a common source of morbidity in patients with measles. Children may experience stomatitis and mouth ulcers over the course of the illness, which may lead to limited oral intake and consequent dehydration.32,33 Diarrhea is a frequent complication.
Most importantly, children with an already tenuous nutritional status are in grave danger from measles infection. Vitamin A deficiency may seriously complicate measles infection in poorly fed or malnourished children, and this deficit is only exacerbated by malabsorption due to diarrhea following the main viral illness.22,23,34 One of the most serious consequences of vitamin A deficiency is the disruption of the corneal surface and the eventual formation of keratomalacia, which may be facilitated by measles keratitis during the viral illness.35 The unfortunate result of this may be lifelong blindness, a grave prospect in regions burdened by poverty and poor education.
Central nervous system (CNS) complications are dominated by three main entities, each characterized by a separate time course of onset. First, and most commonly, children with measles are at risk for post-measles encephalomyelitis. This may occur in one of every 1,000 cases of measles, most frequently affecting older children and adults who have contracted the virus.22,31,36 Affected patients may develop fevers, seizures, altered mental status, and encephalopathy, along with potential focal neurologic abnormalities.37 Of those affected, 20% to 40% may experience permanent neurologic sequelae, such as intellectual disabilities, and 10% to 30% may die.22
A much rarer CNS complication is that of subacute measles encephalitis, also known as measles inclusion body encephalitis. This should not be confused with subacute sclerosing panencephalitis, which will be discussed next. Subacute measles usually occurs among those with impaired cellular immunity and develops within one year of the initial infection.38-40 Patients experience worsening lethargy, altered mental status, and seizures, leading eventually to coma and death within weeks to months of onset. Mortality is extremely high (75%), and there is no effective treatment.
Finally, practitioners should understand the long-term CNS complication of measles: subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE). This is an extremely rare, albeit devastating, complication (one in 1 million cases of measles), and it arises five to 15 years after initial infection.1,22,23 A recent case series in the United States in the post-vaccination era estimates a much higher incidence, ranging from one in 600 to one in 1,000 cases, depending on the age at which the initial measles disease occurred.41 SSPE most often affects those who contracted the disease before 2 years of age, with an even higher incidence if the disease is contracted before 1 year of age. It is typified by seizures and slow deterioration of cognitive and motor functions, characterized on electroencephalogram by generalized, slow-wave complexes. Death inevitably occurs within two years of onset.
Other complications of measles include “black” measles, which is a fulminant hemorrhagic process defined by disseminated intravascular coagulation in malnourished infants in developing countries. This manifestation is poorly understood and rarely seen today.22,23 Other complications not already discussed include measles ophthalmic keratitis, labyrinthitis, secondary bacterial mastoiditis and pharyngitis, myocarditis, pericarditis, transient hepatitis, mesenteric lymphadenitis, thrombocytopenic purpura, and Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Diagnosis
Practitioners have three main options for the laboratory diagnosis of measles infection. These consist of the detection of host serologic response through the production of measles-specific immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibodies, the demonstration of a four-fold increase in immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody titers between acute and convalescent serum specimens, or the detection of viral ribonucleic acid (RNA) through polymerase chain reaction (PCR).19
Realistically, practitioners should always contact their regional health department to discuss the best locally available methods for laboratory diagnosis. This is partly because of the important public health ramifications of positive results, but also to ensure that all public health authorities have access to efficient, consistent evidence of outbreaks across populations.
Historically, collection of serologic evidence of infection (the presence of measles-specific IgM, or a fourfold increase in IgG titers collected 10 days apart) predominated in laboratory diagnosis, but reverse-transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) has become the preferred method in most settings. Viral RNA may be detected in blood, upper and lower respiratory tract samples (such as nasal, throat, or even bronchial lavage specimens), and urine, and the likelihood of viral RNA detection rises with the greater number of samples obtained.19 Practitioners should strive to obtain serum, throat swab, and urine samples for RT-PCR in all suspected cases of measles virus infection, and it is prudent to collect an additional serum sample for IgM assay.
The IgM assay may be positive for up to one month following rash onset, but previously immunized hosts may have a modified serologic picture, and thus the presence of IgM may be absent or transient. Moreover, up to 20% of IgM assays may be falsely negative in the first 72 hours after the onset of rash, meaning that a negative IgM assay may not rule out measles virus infection.19 In cases highly suspicious for measles, or with rash lasting more than 72 hours, a second IgM assay should be sent. Acute and convalescent IgG assays, collected at least 10 days apart, are considered positive if there is a fourfold or greater rise in titers.
Treatment
There is no definitive therapy available for measles infection. Providers should focus their efforts on providing supportive care and antipyretics to make the afflicted child more comfortable.
Vitamin A supplementation is reported to decrease the severity of the illness and reduce mortality; its role is particularly important in developing countries and among children who are malnourished or immunodeficient.19,22,23 Infants 0-6 months of age should receive 50,000 IU of vitamin A once daily for two days; infants 6-11 months of age should receive 100,000 IU once daily for two days; and children 12 months of age or older should receive 200,000 IU once daily for two days.19
In addition, providers should be vigilant against bacterial superinfection, usually in the form of pneumonia. Antibiotic therapy is warranted in such situations, typically targeting organisms consistent with community-acquired pneumonia (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae, targeted with amoxicillin, ampicillin, or ceftriaxone). Prophylactic antibiotics against secondary pneumonia or bacterial superinfection have not been demonstrated to be beneficial.
Prevention, Immunization, and Prophylaxis
Any suspected active measles case in a healthcare setting should activate local infection prevention services for policies regarding isolation. In general, airborne precautions are recommended.20 Local public health departments should be notified and consulted for surveillance and contact tracing. Unimmunized individuals who cannot receive the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine should be excluded from school, childcare, and healthcare settings until 21 days after the onset of rash in the last case of measles documented during an outbreak.19 (See Table 1.)
Table 1. CDC Recommendations on Vaccination for the Prevention of Measles, Mumps, and Rubella |
||
Age 12-15 months: First dose of measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine* |
Age 4-6 years: Second dose of MMR vaccine OR combined measles-mumps-rubella-varicella (MMRV) vaccine** |
Individuals at risk in outbreaks of mumps virus: Third dose of MMR vaccine*** |
*Children 6-11 months of age about to undertake international travel or in outbreak situations may be protected by a dose of MMR vaccine given early, ideally two weeks prior to travel. Any doses of MMR vaccine given before 12 months of age are not considered valid for lifetime immunization, and the child still should receive at least two doses of vaccine on or after the first birthday. **The second dose of MMR vaccine may be given earlier than age 4 years, especially in outbreak situations or prior to international travel, as long as the interval between MMR vaccine doses is at least 28 days. MMRV should not be administered to children under 12 months of age and should be given with a minimum interval between doses of 90 days. ***Persons previously vaccinated with at least two doses of MMR vaccine may be protected by a third dose of MMR vaccine during outbreaks of mumps virus. Further doses of MMR vaccine following the third dose are not recommended. Sources: McLean HQ, Fiebelkorn AP, Temte JL, et al. Prevention of measles, rubella, congenital rubella syndrome, and mumps, 2013: Summary recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep 2013;62:1-34. Marin M, Broder KR, Temte JL, et al. Use of combination measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella vaccine: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep 2010;59:1-12. |
||
Immunization at the individual and population levels is essential for measles prevention. With one dose, the MMR vaccine provides an estimated 93% protection rate against virus transmission; with two doses, the protection rate rises to 97%.42 Children should receive their first dose of MMR at 12-15 months of age, and the second dose (in the form of MMR or combined measles-mumps-rubella-varicella vaccine, or MMRV) at 4-6 years of age. At least 95% of the population must be immunized with the vaccine to disrupt transmission completely and ensure the phenomenon of “herd immunity,” in which those who cannot receive the vaccine for medical reasons are protected from virus acquisition by the immunity of others.43
Contraindications to measles vaccination include immunocompromising conditions, such as chemotherapy, hematologic malignancy, immunosuppression following organ or bone marrow transplant, congenital immunodeficiency, and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and depressed CD4 cell counts.44 Pregnant women should not receive the vaccine. Any prior history of anaphylaxis to measles vaccine is a contraindication. Those who have received immunoglobulin within the past 11 months may not respond to vaccination.
Of note, infants between 6 and 12 months of age traveling to measles-endemic regions or regions at risk of outbreaks should be offered measles vaccination.11 Note that such infants still should receive two doses after 12 months of age, since any dose prior to this age does not count toward the two doses recommended for immunity.
Postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) should be provided for those without evidence of immunity when they are exposed to a case of active measles disease. For immunocompetent individuals older than 6 months of age, the measles vaccine can be given within 72 hours of exposure and may prevent or modify the disease’s course.11 As mentioned earlier, infants older than 6 months of age still should receive two doses after 12 months of age, since any dose prior to this age does not count toward the two doses recommended for immunity.
For those who cannot receive or respond to the live measles vaccine (e.g., pregnant women, the immunocompromised, infants younger than 6 months of age), immunoglobulin is available for PEP and should be given within six days of exposure.11 Intramuscular immunoglobulin (IMIG) should be given to all infants younger than 6 months of age exposed to active measles. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) should be offered to pregnant women and immunocompromised people exposed to active measles.
Those who receive PEP in the form of the measles vaccine within 72 hours of exposure may return to school, childcare, and work (but not healthcare), as long as they are afebrile and feeling well.11 Healthcare personnel require greater caution; regardless of PEP vaccine receipt or immunoglobulin, those without prior immunity must be excluded from healthcare duties from day 5 after first exposure through day 21 after last exposure.
Mumps
Past/Global Epidemiology
In the pre-vaccine era, mumps outbreaks in the United States occurred on a regular, yearly basis among populations of young children, with seasonal peaks in winter and spring and major surges every four years.45 Outbreaks also occurred among older individuals who previously had been isolated from the virus, such as among recruits in the military. The highest recorded rate of mumps acquisition was noted in 1944, when U.S. cases reached 250 per 100,000.45,46
Predictably, the introduction of mumps vaccine in the late 1960s and early 1970s led to decreases in cases among young children, with a consequent shift in the average age of acquisition to older schoolchildren, in part because these patients had not received the vaccine, and as a result of waning immunity from past doses.45,47
The years 1968-1982 illustrate a major triumph for vaccination and public health policy, as the United States experienced a 97% decrease in mumps cases.47 By the 1990s, U.S. cases had decreased to 1,537 cases total in 1994, with 21.8% of cases in patients 20 years of age or older. The number of cases reached an all-time low in 2001-2003 in the United States, when fewer than 300 cases were reported each year.48,49
Present Outbreaks
The mumps virus has found numerous footholds across the United States. In recent decades, increasing numbers of cases have been reported in a variety of local and regional outbreaks.50 The virus has found ready purchase among adolescents and young adults with potentially waning immunity, spurred by larger pools of unvaccinated individuals.
The largest outbreak of the past 20 years occurred in 2006 in the Midwest, affecting 6,584 individuals, many of whom were college students with two prior doses of mumps immunization.51 Further outbreaks took place in 2009-2010, with more than 3,000 cases spreading through the Orthodox Jewish community in New York (many of whom, but not all, were appropriately immunized), and in the U.S. territory of Guam, affecting 500 school-age children.52,53
From 2015 to 2017, at least 150 other outbreaks spread throughout the United States, ranging in size from 10 to more than 3,000 individuals affected.50 These included further outbreaks among several hundred university students in different college settings, as well as more than 3,000 cases in the Marshallese community in Arkansas.54
Similar to measles, decreases in vaccine coverage are predicted to increase pediatric populations’ vulnerability to mumps outbreaks. As of June 2022, 85 mumps cases have been reported in 27 jurisdictions in the United States.50
There are common elements to many of the mumps virus outbreaks described in the post-vaccination era. First, mathematical models predict that, depending on the community and modeling methods used, 70% to 96% vaccination rates in populations are essential to maintain herd immunity and break the chain of transmission.55-57 As antivaccination movements and misinformation have spread on the Internet, such groups have learned to target marginalized and traditionally insular religious or ethnic communities using simplified messages predicated on fear and conspiracy theories, leading to “hotspots” of decreased vaccination and compromised herd immunity.58-60
Second, the mumps component of the MMR is about 78% effective when one dose is given, and 88% effective when children receive the two recommended doses.61 However, there is evidence to indicate that immunity may wane over time, and because of decreased herd immunity, outbreaks may occur in previously immunized populations, especially older adolescents and young adults.62
Third, as with many communicable diseases, transmission is favored by close contact and crowded living conditions, thus many outbreaks have been recorded in groups where large household sizes or crowding is the norm, as well as in college dormitories.63
Typical Clinical Manifestations
Mumps virus is acquired most readily through the upper respiratory epithelia, where primary viral replication occurs.64 Invasion of local lymph nodes follows with subsequent viremia, which leads to the infection of secondary sites, where patients may experience complications.65,66 The total incubation period from the time of acquisition to the onset of clinical symptoms is generally about two weeks, although this may range as widely as 12 to 25 days.45,67
Children initially may experience a prodromal period of one to two days, marked by nonspecific, flu-like symptoms, such as fever, headache, vomiting, myalgias, and anorexia.45 This is followed by parotid gland enlargement. (See Figures 2 and 3.) The majority of patients (70% to 80%) will experience bilateral parotid gland involvement, although unilateral disease does occur.
Figure 2. Parotid Gland Enlargement |
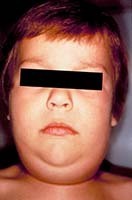 |
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Public Health Image Library |
Figure 3. Left Parotitis from Mumps in an Adult |
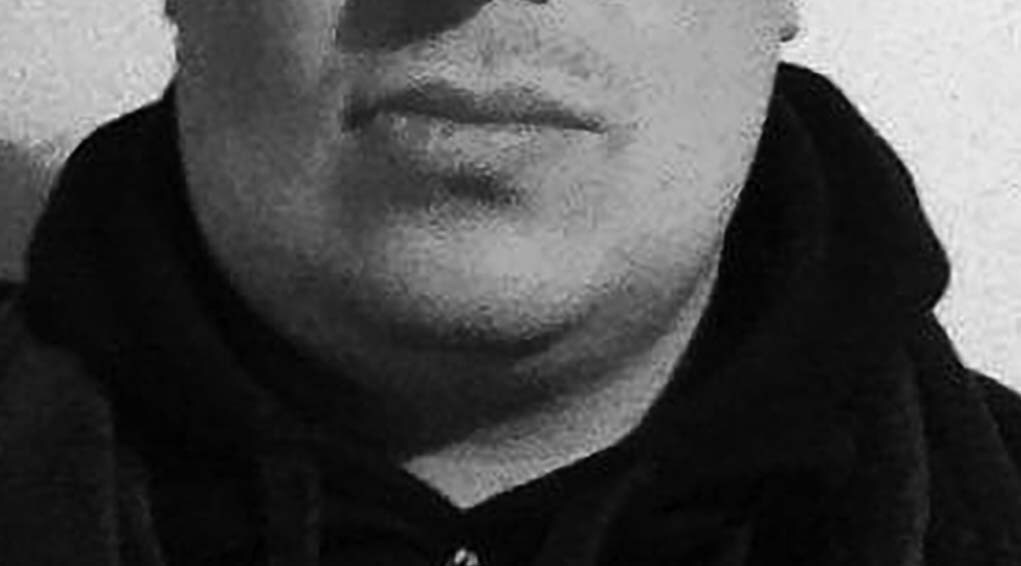 |
Source: Caolan Boyle, Wikimedia Commons. https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/ |
Parotid gland enlargement may be difficult to discern visually from simple lymphadenitis, but the practitioner can attempt to distinguish the two by noting the texture and outline of the swelling on palpation (parotitis is a “brawny” edema with vague borders and loss of the angle of the mandible, whereas lymphadenitis may have clearer boundaries), and by noting the patient’s sensation when inducing a salivary response (the application of sour liquid on the tongue may cause a “puckering” or painful reaction in the parotid gland).45
The meatus of Stenson’s duct on the buccal mucosa also may be erythematous.68 In distinguishing viral parotitis from bacterial parotitis, practitioners may attempt to “milk” the duct by compressing the parotid gland and seeing if pus is excreted from Stenson’s duct. This maneuver is obviously difficult, if not impossible, in younger children, but it may clarify the differential in older children and adults.
Parotitis is accompanied by a painful pressure-like sensation, as well as trismus, because of the diffuse swelling of the gland. This swelling reaches its maximum after three days and typically fades within five to seven days of onset.45,68 Also of note, other salivary glands may be affected, such as the submaxillary or sublingual glands. Even after resolution of adenitis, viral shedding may ensue from parotid and salivary glands for the following two weeks.
Laboratory investigations in uncomplicated mumps may reveal a normal or decreased white blood cell count, perhaps with a relative lymphocytosis.45 Serum amylase may be elevated, which is reasonably caused by salivary gland disease, but also may be the result of pancreatitis. Even in uncomplicated disease, patients may have a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pleocytosis, since mild aseptic meningitis is extremely common.45,68
Complications
Prior to the introduction of the MMR vaccine, the most common cause of aseptic meningitis in infants and children was the mumps virus.69,70 Meningitis and meningoencephalitis may span a range of symptoms, from relatively mild to ependymitis with hydrocephalus.71-74 Younger children with mumps meningitis/meningoencephalitis generally have more nonspecific symptoms of drowsiness and lethargy, whereas older children may develop more classic signs of nuchal rigidity. Seizures may occur in up to 20% to 30% of cases.45 CSF glucose usually is normal, and mild mononuclear pleocytosis (250 white blood cells [WBC]/mm3 to 1,000 WBC/mm3) is common.
Epididymo-orchitis and oophoritis are important complications among adolescents, particularly postpubertal children and young adults. In postpubertal boys, up to 40% or more of cases may experience orchitis.56,75 Such cases usually appear within eight days of parotitis, but late presentation up to six weeks later has been reported.
Orchitis may be characterized by fevers, chills, and swelling of one or both testes, with pain over the renal area or lower abdomen. Testicular tenderness can persist for several weeks in a small proportion of cases.75 Atrophy and sterility, particularly following bilateral disease, are pertinent long-term sequelae. In postpubertal girls, oophoritis may complicate 5% to 7% of mumps cases, marked by pelvic pain and tenderness.45,56
Mumps pancreatitis may occur in 3% of all cases, and it usually is mild or subclinical.76 Patients may experience epigastric pain, tenderness, fever, chills, and vomiting. Temporal association of diabetes mellitus following mumps virus infection has been reported, hypothetically because of islet cell destruction in pancreatitis, but a causal association has not been established.45
Mumps-associated deafness also has been reported following clinical disease, even in the absence of meningoencephalitis.45,56,68 Other less common complications of mumps virus infections include nephritis, fetal loss during pregnancy, myocarditis, and other glandular diseases, such as thyroiditis, mastitis, dacryoadenitis, and bartholinitis.
Diagnosis/Treatment
Mumps may be diagnosed clinically in outbreak or epidemic situations because of its relatively straightforward presentation. However, the confirmation of mumps cases in isolated or sporadic cases can be essential, from both a public health standpoint as well as a medical perspective. Nucleic acid amplification can most easily detect mumps virus from saliva or cheek swabs because of the high levels of viral replication within salivary and parotid gland tissue after two or three days of symptoms.56,77
CSF also is readily assayed by PCR for mumps virus in cases of meningoencephalitis. Acute and convalescent sera also may be assayed for the presence of IgM or an associated rise in IgG antibody titers, although both strategies are problematic and unreliable.45,77 Providers should note that there may be no reliable rise in IgM antibodies among previously immunized individuals, and IgG titers may be so high as to make detection of further rise difficult.
As with measles virus infections, practitioners should always contact their regional health department to discuss the best locally available methods for laboratory diagnosis.
Supportive care is indicated for mumps virus infections.45,77 Analgesics may provide some relief from headaches and parotitis. The viral infection ultimately is self-limited, and currently there is no antiviral therapy approved for treatment of the acute course or its associated complications.
Prevention and Immunization
Infection prevention services always should be activated for any suspected active mumps case in a healthcare setting. Standard and droplet precautions are recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.78 As mentioned earlier, regional public health departments should be notified and consulted for guidance regarding preferred diagnostic testing and for surveillance purposes.
All susceptible children, adolescents, and adults without contraindications should receive two doses of mumps vaccine.78,79 Individuals without a history of physician-diagnosed mumps, proof of two vaccines on or after the first birthday, or laboratory evidence of immunity are considered susceptible. With one dose, the MMR vaccine provides an estimated 78% protection rate against mumps virus transmission; with two doses, the protection rate rises to 88%.78 As discussed previously, children should receive their first dose of MMR at 12-15 months of age, and the second dose (in the form of MMR or combined MMRV vaccine) at 4-6 years of age.
As mentioned previously, contraindications to MMR vaccination include immunocompromising conditions, such as chemotherapy, hematologic malignancy, immunosuppression following organ or bone marrow transplant, congenital immunodeficiency, and HIV and depressed CD4 cell counts.44 Pregnant women should not receive the vaccine. Any prior history of anaphylaxis to the MMR vaccine is a contraindication. Those who have received immunoglobulin within the past 11 months may not respond to vaccination, depending on the dosage and indications of prior immunoglobulin receipt.
PEP with a third dose of MMR is not routinely recommended. However, in institutional settings with close contact or in close-knit communities, a third dose of the MMR vaccine administered during an outbreak reduces the spread of disease and the number of cases.80 Thus, a third MMR dose should be considered in mumps outbreaks at schools or universities.
Those with active mumps disease should be excluded from work and school for at least five days from onset of parotid gland swelling.77
Conclusion
Global pediatric and adolescent populations are increasingly vulnerable and threatened by measles and mumps outbreaks, particularly with the drops of vaccine coverage induced by the COVID-19 pandemic since early 2020. In addition, antivaccination campaigns have led some communities to forgo vaccination because of unfounded fears about vaccine safety.
Measles is responsible for more than 100,000 deaths per year globally.81 It is one of the most infectious agents known to humanity. Many children who survive the disease will experience significant morbidity and, in some cases, disability as the result of encephalitis. The measles vaccine is the most effective tool to prevent disease and disrupt transmission.
Mumps, while clinically dissimilar with a lower burden of mortality and morbidity, potentially still may lead to significant morbidity and long-term effects in children. Vaccination is the most effective means of preventing the disease and disrupting transmission, but in certain populations with outbreaks, even those with two prior doses of vaccine may develop the illness, and providers and public health departments should consider providing third doses of vaccines to those in institutional settings with close contact or close-knit communities.
The resurgence of preventable diseases, especially those that previously have been eliminated from an endemic status, such as measles, is facilitated by widening circles of misinformation on social media and the Internet. Physicians and providers bear duties to their patients, but in the broader context of public health, must work to dispel myths and rumors regarding immunization and disease prevention.
REFERENCES
- Moss WJ. Measles. Lancet 2017;390: 2490-2502.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Transmission of measles. Last reviewed Nov. 5, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/transmission.html
- Althaus CL. Estimating the reproduction number of Ebola virus (EBOV) during the 2014 outbreak in West Africa. PLoS Curr 2014;6:ecurrents.outbreaks.91afb5e0f279e7f29e7056095255b288.
- Liu Y, Rocklöv J. The reproductive number of the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 is far higher compared to the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 virus. J Travel Med 2021;28:taab124.
- Guerra FM, Bolotin S, Lim G, et al. The basic reproduction number (R0) of measles: A systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis 2017;17:e420-e428.
- Fine PE, Clarkson JA. Measles in England and Wales—I: An analysis of factors underlying seasonal patterns. Int J Epidemiol 1982;11:5-14.
- Shulman ST, Shulman DL, Sims RH. The tragic 1824 journey of the Hawaiian king and queen to London: History of measles in Hawaii. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2009;28:728-733.
- Panum PL. Observations made during the epidemic of measles on the Faroe Islands in the year 1846. http://www.med.mcgill.ca/epidemiology/courses/EPIB591/Fall%202010/mid-term%20presentations/Paper9.pdf
- Guerra F. The European-American exchange. Hist Philos Life Sci 1993;15:313-327.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles history. Last reviewed Nov. 5, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/about/history.html
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. For healthcare professionals. Last reviewed Nov. 5, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/hcp/index.html
- Hall-Baker PA, Nieves E Jr, Jajosky RA, et al. Summary of notifiable diseases —United States, 2008. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2010;57:1-94.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Measles: United States, January-May 20, 2011. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2011;60:666-668.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles cases and outbreaks. Last reviewed Oct. 3, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/cases-outbreaks.html
- Gastañaduy PA, Budd J, Fisher N, et al. A measles outbreak in an underimmunized Amish community in Ohio. N Engl J Med 2016;375:1343-1354.
- Zipprich J, Winter K, Hacker J, et al. Measles outbreak — California, December 2014-February 2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2015;64:153-154. Erratum in: MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2015;64:196.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Global measles outbreaks. Updated June 13, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/globalhealth/measles/data/global-measles-outbreaks.html
- de Vries RD, Mesman AW, Geijtenbeek TBH, et al. The pathogenesis of measles. Curr Opin Virol 2012;2:248-255.
- Measles. In: Kimberlin DW, Brady MT, Jackson MA, Long SS, eds. Red Book 2021-2024 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases. 32nd ed. American Academy of Pediatrics; 2021.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim infection prevention and control recommendations for measles in healthcare settings. Last reviewed July 23, 2019. https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/measles/index.html
- Ludlow M, McQuaid S, Milner D, et al. Pathological consequences of systemic measles virus infection. J Pathol 2015;235:253-265.
- Cherry JD, Lugo D. Measles virus. In: Cherry JD, Harrison GJ, Kaplan SL, et al, eds. Feigin and Cherry’s Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2019.
- Gershon AA. Measles virus (rubeola). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2015.
- Azizi A, Krakovsky D. Kerato-conjunctivitis as a constant sign of measles. Ann Paediatr 1965;204:397-405.
- Lefebvre N, Camuset G, Bui E, et al. Koplik spots: A clinical sign with epidemiological implications for measles control. Dermatology 2010;220:280-281.
- Koplik H. The diagnosis of the invasion of measles from a study of the exanthemata as it appears on the buccal mucous membranes. Arch Pediatr (N Y) 1962;79:162-165.
- Gastanaduy P, Haber P, Rota PA, Patel M. Measles. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Last reviewed Aug. 18, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/pinkbook/meas.html#vaccines
- Melenotte C, Cassir N, Tessonnier L, Brouqui P. Atypical measles syndrome in adults: Still around. BMJ Case Rep 2015;2015:bcr2015211054.
- Kohn JL, Koiransky H. Successive roentgenograms of the chest of children during measles. Am J Dis Child 1929;38:258-270.
- Barkin RM. Measles mortality. Analysis of the primary cause of death. Am J Dis Child 1975;129:307-309.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Complications of measles. Last reviewed Nov. 5, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/symptoms/complications.html
- Morley DC. Measles in Nigeria. Am J Dis Child 1962;103:230-233.
- Morley D, Woodland M, Martin WJ. Measles in Nigerian children: A study of the disease in West Africa, and its manifestations in England and other countries during different epochs. J Hyg (Lond) 1963;61:115-134.
- Stevens GA, Bennett JE, Hennocq Q, et al. Trends and mortality effects of vitamin A deficiency in children in 138 low-income and middle-income countries between 1991 and 2013: A pooled analysis of population-based surveys. Lancet Glob Health 2015;3:e528-e536.
- Sandford-Smith JH, Whittle HC. Corneal ulceration following measles in Nigerian children. Br J Ophthalmol 1979;63:720-724.
- Griffin DE. Measles virus and the nervous system. Handb Clin Neurol 2014;123:577-590.
- Laboccetta AC, Tornay AS. Measles encephalitis. Report of 61 cases. Am J Dis Child 1964;107:247-255.
- Baldolli A, Dargere S, Cardineau E, et al. Measles inclusion-body encephalitis (MIBE) in a immunocompromised patient. J Clin Virol 2016;81:43-46.
- Fisher DL, Defres S, Solomon T. Measles-induced encephalitis. QJM 2015;108:177-182.
- Mustafa MM, Weitman SD, Winick NJ, et al. Subacute measles encephalitis in the young immunocompromised host: Report of two cases diagnosed by polymerase chain reaction and treated with ribavirin and review of the literature. Clin Infect Dis 1993;16:654-660.
- Wendorf KA, Winter K, Zipprich J, et al. Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis: The devastating measles complication that might be more common than previously estimated. Clin Infect Dis 2017;65:226-232.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Vaccine for measles. Last reviewed Nov. 5, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/vaccination.html
- van Boven M, Kretzschmar M, Wallinga J, et al. Estimation of measles vaccine efficacy and critical vaccination coverage in a highly vaccinated population. J R Soc Interface 2010;7:1537-1544.
- Kroger A, Bahta L, Hunter P. General best practice guidelines for immunization. General Best Practice Guidelines for Immunization. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Last reviewed March 15, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/general-recs/index.html
- Cherry JD, Quinn KK. Mumps virus. In: Cherry JD, Harrison GJ, Kaplan SL, et al, eds. Feigin and Cherry’s Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2019.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Mumps — United States, 1983-1984. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 1984;33:533-535.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Current trends mumps — United States, 1980-1983. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 1983;32:545-547.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Summary of notifiable diseases — United States, 2013. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2015;62:1-119.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Mumps epidemic — Iowa, 2006. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2006;55:366-368.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Mumps cases and outbreaks. https://www.cdc.gov/mumps/outbreaks.html
- Dayan GH, Quinlisk MP, Parker AA, et al. Recent resurgence of mumps in the United States. N Engl J Med 2008;358:1580-1589.
- Barskey AE, Schulte C, Rosen JB, et al. Mumps outbreak in Orthodox Jewish communities in the United States. N Engl J Med 2012;367:1704-1713.
- Nelson GE, Aguon A, Valencia E, et al. Epidemiology of a mumps outbreak in a highly vaccinated island population and use of a third dose of measles-mumps-rubella vaccine for outbreak control — Guam 2009 to 2010. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2013;32:374-380.
- Fields VS, Safi H, Waters C, et al. Mumps in a highly vaccinated Marshallese community in Arkansas, USA: An outbreak report. Lancet Infect Dis 2019;19:185-192.
- Majumder MS, Nguyen CM, Cohn EL, et al. Vaccine compliance and the 2016 Arkansas mumps outbreak. Lancet Infect Dis 2017;17:361-362.
- Hviid A, Rubin S, Muhlemann K. Mumps. Lancet 2008;371:932-944.
- Edmunds WJ, Gay NJ, Kretzschmar M, et al. The pre-vaccination epidemiology of measles, mumps and rubella in Europe: Implications for modelling studies. Epidemiol Infect 2000;125:635-650.
- Smith L. How the anti-vaccine movement targets cities – and creates disease ‘hotspots.’ The Guardian. Published March 14, 2019. https://www.theguardian.com/cities/2019/mar/14/are-urban-anti-vaccine-hotspots-putting-children-at-risk
- Osterholm M. The measles outbreak: Unfounded fears about vaccine put kids at risk. The Star Tribune. Published May 4, 2017. http://www.startribune.com/the-measles-outbreak-unfounded-fears-about-vaccine-put-kids-at-risk/421224433/
- Dubé E, Vivion M, MacDonald NE. Vaccine hesitancy, vaccine refusal and the anti-vaccine movement: Influence, impact and implications. Expert Rev Vaccines 2015;14:99-117.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. For healthcare providers. Last reviewed March 8, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mumps/hcp.html
- Kennedy RB, Ovsyannikova IG, Thomas A, et al. Differential durability of immune responses to measles and mumps following MMR vaccination. Vaccine 2019;37:1775-1784.
- Cortese MM, Jordan HT, Curns AT, et al. Mumps vaccine performance among university students during a mumps outbreak. Clin Infect Dis 2008;46:1172-1180.
- Foy HM, Cooney MK, Hall CE, et al. Isolation of mumps virus from children with acute lower respiratory tract disease. Am J Epidemiol 1971;94:467-472.
- Kilham L. Isolation of mumps virus from the blood of a patient. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 1948;69:99.
- Overman JR. Viremia in human mumps virus infections. AMA Arch Intern Med 1958;102:354-356.
- Richardson M, Elliman D, Maguire H, et al. Evidence base of incubation periods, periods of infectiousness and exclusion policies for the control of communicable diseases in schools and preschools. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2001;20:380-391.
- Litman N. Mumps virus. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2015.
- Davison KL, Ramsay ME. The epidemiology of acute meningitis in children in England and Wales. Arch Dis Child 2003;88:662-664.
- Rantakallio P, Leskinen M, von Wendt L. Incidence and prognosis of central nervous system infections in a birth cohort of 12,000 children. Scand J Infect Dis 1986;18:287-294.
- Murray HG, Field CM, McLeod WJ. Mumps meningoencephalitis. Br Med J 1960;1:1850-1853.
- Azimi PH, Cramblett HG, Haynes RE. Mumps meningoencephalitis in children. JAMA 1969;207:509-512.
- Levitt LP, Rich TA, Kinde SW, et al. Central nervous system mumps. A review of 64 cases. Neurology 1970;20:829-834.
- Uno M, Takano T, Yamano T, Shimada M. Age-dependent susceptibility in mumps-associated hydrocephalus: Neuropathologic features and brain barriers. Acta Neuropathol 1997;94:207-215.
- Davis NF, McGuire BB, Mahon JA, et al. The increasing incidence of mumps orchitis: A comprehensive review. BJU Int 2010;105:1060-1065.
- The Association for the Study of Infectious Disease. A retrospective survey of the complications of mumps. J R Coll Gen Pract 1974;24:552-556.
- Marlow M, Leung J, Marin M, et al. Mumps. In: Kimberlin DW, Brady MT, Jackson MA, Long SS, eds. Red Book 2021-2024 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases. 32nd ed. American Academy of Pediatrics; 2021.
- Marlow M, Leung J, Marin M, et al. Chapter 9: Mumps. In: Roush SW, Baldy LM, Hall MAK, eds. Manual for the Surveillance of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- McLean HQ, Fiebelkorn AP, Temte JL, et al. Prevention of measles, rubella, congenital rubella syndrome, and mumps, 2013: Summary recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep 2013;62:1-34.
- Marin M, Marlow M, Moore KL, Patel M. Recommendation of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices for use of a third dose of mumps virus–
containing vaccine in persons at increased risk for mumps during an outbreak. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2018;67:33-38. - World Health Organization. Measles. Published Dec. 5, 2019. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/measles
Decreased vaccine coverage against diseases such as measles and mumps has led to new vulnerabilities in pediatric population health. Thus, the astute practitioner should be vigilant and ready to recognize and diagnose these infections.
Subscribe Now for Access
You have reached your article limit for the month. We hope you found our articles both enjoyable and insightful. For information on new subscriptions, product trials, alternative billing arrangements or group and site discounts please call 800-688-2421. We look forward to having you as a long-term member of the Relias Media community.
